キューに基づく大きなティックサイズ資産のマーケットメイキング
概要
キュー位置の重要性は、特に大きなティックサイズの資産において、ミクロ構造取引でよく知られています。これは、大きなティックサイズの資産が通常、価格変動がより制約されているためです。ティックサイズの影響については、“Large tick assets: implicit spread and optimal tick size”で詳しく説明されています。

注: この例は教育目的のみであり、高頻度マーケットメイキングスキームの効果的な戦略を示しています。すべてのバックテストは、Binance Futuresで利用可能な最高のマーケットメイカーリベートである0.005%のリベートに基づいています。詳細については、Binance Upgrades USDⓢ-Margined Futures Liquidity Provider Program を参照してください。
ブックプレッシャー
まず、Market Microstructure signals described in this articleを確認します。これは、マイクロプライスの概念に似ています。ブックの不均衡については、Market Making with Alpha - Order Book Imbalanceでも取り上げられています。
[1]:
import numpy as np
from numba import njit, uint64, float64
from numba.typed import Dict
from hftbacktest import BUY, SELL, GTX, LIMIT
@njit
def mm_strategy(hbt, recorder):
asset_no = 0
tick_size = hbt.depth(asset_no).tick_size
order_qty = 1
grid_num = 10
max_position = grid_num * order_qty
# Our half spread is just half a tick size,
# but it's considered a round-off error, so we use 0.49, which is slightly less than 0.5.
# If you set a lower value, the order will tend to stay to the best bid and offer, even when book pressure increases.
# You can think of it as a threshold for backing off based on book pressure.
half_spread = tick_size * 0.49
grid_interval = tick_size
skew_adj = 1.0
# Running interval in nanoseconds.
while hbt.elapse(100_000_000) == 0:
# Clears cancelled, filled or expired orders.
hbt.clear_inactive_orders(asset_no)
depth = hbt.depth(asset_no)
position = hbt.position(asset_no)
orders = hbt.orders(asset_no)
last_trades = hbt.last_trades(asset_no)
best_bid = depth.best_bid
best_ask = depth.best_ask
best_bid_qty = depth.bid_depth[depth.best_bid_tick]
best_ask_qty = depth.ask_depth[depth.best_ask_tick]
# Market microstructure signals in https://blog.headlandstech.com/2017/08/
book_pressure = (best_bid * best_ask_qty + best_ask * best_bid_qty) / (best_bid_qty + best_ask_qty)
skew = half_spread / grid_num * skew_adj
normalized_position = position / order_qty
# The personalized price that considers skewing based on inventory risk is introduced,
# which is described in the well-known Stokov-Avalleneda market-making paper.
# https://math.nyu.edu/~avellane/HighFrequencyTrading.pdf
reservation_price = book_pressure - skew * normalized_position
# Since our price is skewed, it may cross the spread. To ensure market making and avoid crossing the spread,
# limit the price to the best bid and best ask.
bid_price = np.minimum(reservation_price - half_spread, best_bid)
ask_price = np.maximum(reservation_price + half_spread, best_ask)
# Aligns the prices to the grid.
bid_price = np.floor(bid_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
ask_price = np.ceil(ask_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
#--------------------------------------------------------
# Updates quotes.
# Creates a new grid for buy orders.
new_bid_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position < max_position and np.isfinite(bid_price):
for i in range(grid_num):
bid_price_tick = round(bid_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_bid_orders[uint64(bid_price_tick)] = bid_price
bid_price -= grid_interval
# Creates a new grid for sell orders.
new_ask_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position > -max_position and np.isfinite(ask_price):
for i in range(grid_num):
ask_price_tick = round(ask_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_ask_orders[uint64(ask_price_tick)] = ask_price
ask_price += grid_interval
order_values = orders.values();
while order_values.has_next():
order = order_values.get()
# Cancels if a working order is not in the new grid.
if order.cancellable:
if (
(order.side == BUY and order.order_id not in new_bid_orders)
or (order.side == SELL and order.order_id not in new_ask_orders)
):
hbt.cancel(asset_no, order.order_id, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_bid_orders.items():
# Posts a new buy order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_buy_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_ask_orders.items():
# Posts a new sell order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_sell_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
# Records the current state for stat calculation.
recorder.record(hbt)
return True
[2]:
from hftbacktest import BacktestAsset, ROIVectorMarketDepthBacktest, Recorder
asset = (
BacktestAsset()
.data([
f'data/CRVUSDT_{date}.npz' for date in range(20240701, 20240732)
] + [
f'data/CRVUSDT_{date}.npz' for date in range(20240801, 20240832)
])
.linear_asset(1.0)
.intp_order_latency([
f'latency/amp_feed_latency_{date}.npz' for date in range(20240701, 20240732)
] + [
f'latency/amp_feed_latency_{date}.npz' for date in range(20240801, 20240832)
])
.power_prob_queue_model(3.0)
.no_partial_fill_exchange()
.trading_value_fee_model(-0.00005, 0.0007)
.tick_size(0.001)
.lot_size(0.1)
.roi_lb(0.0)
.roi_ub(2.0)
.last_trades_capacity(1000)
)
hbt = ROIVectorMarketDepthBacktest([asset])
recorder = Recorder(1, 100_000_000)
[3]:
%%time
mm_strategy(hbt, recorder.recorder)
_ = hbt.close()
CPU times: user 8min 14s, sys: 8.57 s, total: 8min 23s
Wall time: 6min 49s
[4]:
from hftbacktest.stats import LinearAssetRecord
stats = LinearAssetRecord(recorder.get(0)).stats()
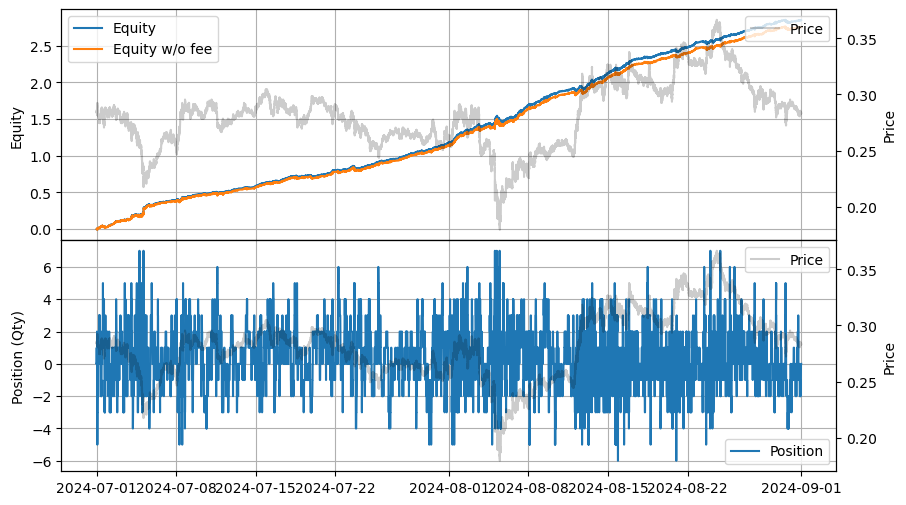
stats.summary()
[4]:
| start | end | SR | Sortino | Return | MaxDrawdown | DailyNumberOfTrades | DailyTradingValue | ReturnOverMDD | ReturnOverTrade | MaxPositionValue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| datetime[μs] | datetime[μs] | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 |
| 2024-07-01 00:00:00 | 2024-08-31 23:59:50 | 16.386564 | 23.90151 | 2.848749 | 0.096359 | 106.774393 | 30.241524 | 29.563923 | 0.001519 | 2.4745 |
[5]:
stats.plot()
トレードインパルス
トレードインパルスを組み込むとどのように変化するかを見てみましょう。
[6]:
from hftbacktest import BUY_EVENT
@njit
def mm_strategy(hbt, recorder):
asset_no = 0
tick_size = hbt.depth(asset_no).tick_size
order_qty = 1
grid_num = 10
max_position = grid_num * order_qty
# Our half spread is just half a tick size,
# but it's considered a round-off error, so we use 0.49, which is slightly less than 0.5.
half_spread = tick_size * 0.49
grid_interval = tick_size
skew_adj = 1.0
trade_impulse_adj = 1.0
sum_bbo_qty = np.empty(50_000_000, float64)
i = 0
# Running interval in nanoseconds.
while hbt.elapse(100_000_000) == 0:
# Clears cancelled, filled or expired orders.
hbt.clear_inactive_orders(asset_no)
depth = hbt.depth(asset_no)
position = hbt.position(asset_no)
orders = hbt.orders(asset_no)
last_trades = hbt.last_trades(asset_no)
best_bid = depth.best_bid
best_ask = depth.best_ask
best_bid_qty = depth.bid_depth[depth.best_bid_tick]
best_ask_qty = depth.ask_depth[depth.best_ask_tick]
# Market microstructure signals in https://blog.headlandstech.com/2017/08/
book_pressure = (best_bid * best_ask_qty + best_ask * best_bid_qty) / (best_bid_qty + best_ask_qty)
# Computes the trade impulse
last_qty = 0
if len(last_trades) > 0:
if last_trades[-1].ev & BUY_EVENT == BUY_EVENT:
last_qty = last_trades[-1].qty
else:
last_qty = -last_trades[-1].qty
hbt.clear_last_trades(asset_no)
sum_bbo_qty[i] = best_bid_qty + best_ask_qty
i += 1
# Uses the last 1-minute average BBO quantity as the denominator.
trade_impulse = (tick_size / 2.0) * last_qty / np.mean(sum_bbo_qty[max(0, i - 600):i])
fair_price = book_pressure + trade_impulse * trade_impulse_adj
skew = half_spread / grid_num * skew_adj
normalized_position = position / order_qty
# The personalized price that considers skewing based on inventory risk is introduced,
# which is described in the well-known Stokov-Avalleneda market-making paper.
# https://math.nyu.edu/~avellane/HighFrequencyTrading.pdf
reservation_price = fair_price - skew * normalized_position
# Since our price is skewed, it may cross the spread. To ensure market making and avoid crossing the spread,
# limit the price to the best bid and best ask.
bid_price = np.minimum(reservation_price - half_spread, best_bid)
ask_price = np.maximum(reservation_price + half_spread, best_ask)
# Aligns the prices to the grid.
bid_price = np.floor(bid_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
ask_price = np.ceil(ask_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
#--------------------------------------------------------
# Updates quotes.
# Creates a new grid for buy orders.
new_bid_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position < max_position and np.isfinite(bid_price):
for i in range(grid_num):
bid_price_tick = round(bid_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_bid_orders[uint64(bid_price_tick)] = bid_price
bid_price -= grid_interval
# Creates a new grid for sell orders.
new_ask_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position > -max_position and np.isfinite(ask_price):
for i in range(grid_num):
ask_price_tick = round(ask_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_ask_orders[uint64(ask_price_tick)] = ask_price
ask_price += grid_interval
order_values = orders.values();
while order_values.has_next():
order = order_values.get()
# Cancels if a working order is not in the new grid.
if order.cancellable:
if (
(order.side == BUY and order.order_id not in new_bid_orders)
or (order.side == SELL and order.order_id not in new_ask_orders)
):
hbt.cancel(asset_no, order.order_id, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_bid_orders.items():
# Posts a new buy order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_buy_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_ask_orders.items():
# Posts a new sell order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_sell_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
# Records the current state for stat calculation.
recorder.record(hbt)
return True
[7]:
hbt = ROIVectorMarketDepthBacktest([asset])
recorder = Recorder(1, 100_000_000)
[8]:
%%time
mm_strategy(hbt, recorder.recorder)
_ = hbt.close()
CPU times: user 8min 13s, sys: 8.03 s, total: 8min 21s
Wall time: 6min 48s
[9]:
stats = LinearAssetRecord(recorder.get(0)).stats()
stats.summary()
[9]:
| start | end | SR | Sortino | Return | MaxDrawdown | DailyNumberOfTrades | DailyTradingValue | ReturnOverMDD | ReturnOverTrade | MaxPositionValue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| datetime[μs] | datetime[μs] | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 |
| 2024-07-01 00:00:00 | 2024-08-31 23:59:50 | 16.52588 | 24.122559 | 2.874579 | 0.096359 | 106.580844 | 30.186685 | 29.831983 | 0.001536 | 2.4745 |
[10]:
stats.plot()
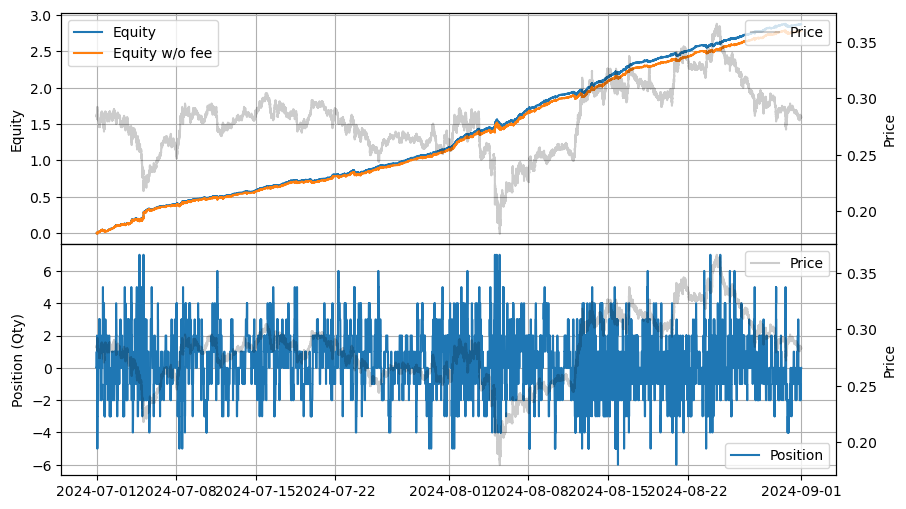
最後の取引数量が最良買い気配値と最良売り気配値の数量に比べて比較的小さいため、大きな違いはありません。

次の例は、集計された取引数量を使用したトレードインパルスのバリエーションを示しています。
[11]:
@njit
def mm_strategy(hbt, recorder):
asset_no = 0
tick_size = hbt.depth(asset_no).tick_size
order_qty = 1
grid_num = 10
max_position = grid_num * order_qty
# Our half spread is just half a tick size,
# but it's considered a round-off error, so we use 0.49, which is slightly less than 0.5.
half_spread = tick_size * 0.49
grid_interval = tick_size
skew_adj = 1.0
trade_impulse_adj = 1.0
sum_bbo_qty = np.empty(50_000_000, float64)
i = 0
# Running interval in nanoseconds.
while hbt.elapse(100_000_000) == 0:
# Clears cancelled, filled or expired orders.
hbt.clear_inactive_orders(asset_no)
depth = hbt.depth(asset_no)
position = hbt.position(asset_no)
orders = hbt.orders(asset_no)
last_trades = hbt.last_trades(asset_no)
best_bid = depth.best_bid
best_ask = depth.best_ask
best_bid_qty = depth.bid_depth[depth.best_bid_tick]
best_ask_qty = depth.ask_depth[depth.best_ask_tick]
# Market microstructure signals in https://blog.headlandstech.com/2017/08/
book_pressure = (best_bid * best_ask_qty + best_ask * best_bid_qty) / (best_bid_qty + best_ask_qty)
# Computes the trading impulse
last_qty = 0
for last_trade in last_trades:
if last_trade.ev & BUY_EVENT == BUY_EVENT:
last_qty += last_trade.qty
else:
last_qty -= -last_trade.qty
hbt.clear_last_trades(asset_no)
sum_bbo_qty[i] = best_bid_qty + best_ask_qty
i += 1
# Uses the last 1-minute average BBO quantity as the denominator.
trade_impulse = (tick_size / 2.0) * last_qty / np.mean(sum_bbo_qty[max(0, i - 600):i])
fair_price = book_pressure + trade_impulse * trade_impulse_adj
skew = half_spread / grid_num * skew_adj
normalized_position = position / order_qty
# The personalized price that considers skewing based on inventory risk is introduced,
# which is described in the well-known Stokov-Avalleneda market-making paper.
# https://math.nyu.edu/~avellane/HighFrequencyTrading.pdf
reservation_price = fair_price - skew * normalized_position
# Since our price is skewed, it may cross the spread. To ensure market making and avoid crossing the spread,
# limit the price to the best bid and best ask.
bid_price = np.minimum(reservation_price - half_spread, best_bid)
ask_price = np.maximum(reservation_price + half_spread, best_ask)
# Aligns the prices to the grid.
bid_price = np.floor(bid_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
ask_price = np.ceil(ask_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
#--------------------------------------------------------
# Updates quotes.
# Creates a new grid for buy orders.
new_bid_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position < max_position and np.isfinite(bid_price):
for i in range(grid_num):
bid_price_tick = round(bid_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_bid_orders[uint64(bid_price_tick)] = bid_price
bid_price -= grid_interval
# Creates a new grid for sell orders.
new_ask_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position > -max_position and np.isfinite(ask_price):
for i in range(grid_num):
ask_price_tick = round(ask_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_ask_orders[uint64(ask_price_tick)] = ask_price
ask_price += grid_interval
order_values = orders.values();
while order_values.has_next():
order = order_values.get()
# Cancels if a working order is not in the new grid.
if order.cancellable:
if (
(order.side == BUY and order.order_id not in new_bid_orders)
or (order.side == SELL and order.order_id not in new_ask_orders)
):
hbt.cancel(asset_no, order.order_id, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_bid_orders.items():
# Posts a new buy order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_buy_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_ask_orders.items():
# Posts a new sell order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_sell_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
# Records the current state for stat calculation.
recorder.record(hbt)
return True
[12]:
hbt = ROIVectorMarketDepthBacktest([asset])
recorder = Recorder(1, 100_000_000)
[13]:
%%time
mm_strategy(hbt, recorder.recorder)
_ = hbt.close()
CPU times: user 8min 13s, sys: 7.99 s, total: 8min 21s
Wall time: 6min 48s
[14]:
stats = LinearAssetRecord(recorder.get(0)).stats()
stats.summary()
[14]:
| start | end | SR | Sortino | Return | MaxDrawdown | DailyNumberOfTrades | DailyTradingValue | ReturnOverMDD | ReturnOverTrade | MaxPositionValue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| datetime[μs] | datetime[μs] | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 |
| 2024-07-01 00:00:00 | 2024-08-31 23:59:50 | 13.831429 | 20.083391 | 2.503742 | 0.114379 | 113.35505 | 32.174754 | 21.889804 | 0.001255 | 2.828 |
[15]:
stats.plot()
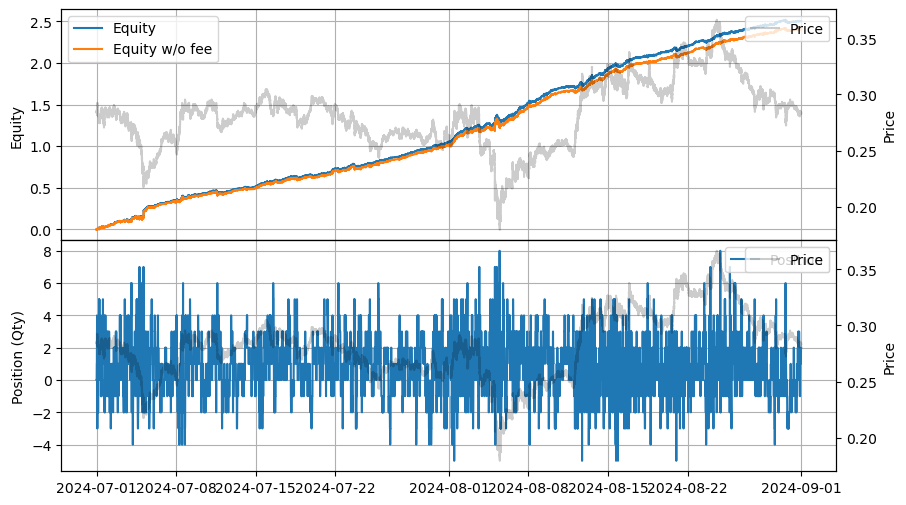
trade_impulse_adjを調整してトレードインパルスの影響を変更することもできます。あるいは、(best_bid * best_ask_qty + best_ask * best_bid_qty + last_px * last_qty) / (best_bid_qty + best_ask_qty + last_qty)、VWAPなど、トレードインパルスを計算する他の方法を探ることもできます。
純粋なキューに基づくモデル
この戦略が利益を生む可能性がある理由の1つは、大きなティックサイズによる価格変動の制限です。たとえば、CRVUSDTのティックサイズは38ベーシスポイント(0.001 / 0.26 * 10,000)であり、BTCUSDTのティックサイズが約0.018ベーシスポイント(0.1 / 54,000 * 10,000)と比較して非常に大きいです。
これはまた、大きなティックサイズの資産のフィルシミュレーションにおけるキュー位置モデリングの重要性を強調しています。
上記のCRVUSDTチャートを観察すると、ほとんどの取引が最良買い気配値と最良売り気配値で行われており、全体的な価格レベルにほとんど変化がないことがわかります。
これは、ミクロ構造信号を純粋にキューに基づく信号に調整する機会を示唆しています。たとえば、価格レベルを維持するのに十分な数量があり、価格が不利に動くのを防ぐことができる場合、私たちのクォートを維持することを選択できます。これがどのように実装できるかを簡略化した形で見てみましょう。
[16]:
@njit
def mm_strategy(hbt, recorder):
asset_no = 0
tick_size = hbt.depth(asset_no).tick_size
order_qty = 1
grid_num = 10
max_position = grid_num * order_qty
# Our half spread is just half a tick size,
# but it's considered a round-off error, so we use 0.49, which is slightly less than 0.5.
half_spread = tick_size * 0.49
grid_interval = tick_size
skew_adj = 1.0
qty_threshold = 250_000
# Running interval in nanoseconds.
while hbt.elapse(100_000_000) == 0:
# Clears cancelled, filled or expired orders.
hbt.clear_inactive_orders(asset_no)
depth = hbt.depth(asset_no)
position = hbt.position(asset_no)
orders = hbt.orders(asset_no)
last_trades = hbt.last_trades(asset_no)
best_bid = depth.best_bid
best_ask = depth.best_ask
best_bid_qty = depth.bid_depth[depth.best_bid_tick]
best_ask_qty = depth.ask_depth[depth.best_ask_tick]
skew = half_spread / grid_num * skew_adj
normalized_position = position / order_qty
skew_val = skew * normalized_position
if best_bid_qty < qty_threshold and skew_val > 0:
bid_price = best_bid - tick_size
else:
bid_price = best_bid
if best_ask_qty < qty_threshold and skew_val < 0:
ask_price = best_ask + tick_size
else:
ask_price = best_ask
# Aligns the prices to the grid.
bid_price = np.floor(bid_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
ask_price = np.ceil(ask_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
#--------------------------------------------------------
# Updates quotes.
# Creates a new grid for buy orders.
new_bid_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position < max_position and np.isfinite(bid_price):
for i in range(grid_num):
bid_price_tick = round(bid_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_bid_orders[uint64(bid_price_tick)] = bid_price
bid_price -= grid_interval
# Creates a new grid for sell orders.
new_ask_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position > -max_position and np.isfinite(ask_price):
for i in range(grid_num):
ask_price_tick = round(ask_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_ask_orders[uint64(ask_price_tick)] = ask_price
ask_price += grid_interval
order_values = orders.values();
while order_values.has_next():
order = order_values.get()
# Cancels if a working order is not in the new grid.
if order.cancellable:
if (
(order.side == BUY and order.order_id not in new_bid_orders)
or (order.side == SELL and order.order_id not in new_ask_orders)
):
hbt.cancel(asset_no, order.order_id, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_bid_orders.items():
# Posts a new buy order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_buy_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_ask_orders.items():
# Posts a new sell order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_sell_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
# Records the current state for stat calculation.
recorder.record(hbt)
return True
[17]:
hbt = ROIVectorMarketDepthBacktest([asset])
recorder = Recorder(1, 100_000_000)
[18]:
%%time
mm_strategy(hbt, recorder.recorder)
_ = hbt.close()
CPU times: user 8min 16s, sys: 8.52 s, total: 8min 24s
Wall time: 6min 51s
[19]:
stats = LinearAssetRecord(recorder.get(0)).stats()
stats.summary()
[19]:
| start | end | SR | Sortino | Return | MaxDrawdown | DailyNumberOfTrades | DailyTradingValue | ReturnOverMDD | ReturnOverTrade | MaxPositionValue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| datetime[μs] | datetime[μs] | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 |
| 2024-07-01 00:00:00 | 2024-08-31 23:59:50 | 13.199337 | 18.042325 | 3.95075 | 0.18009 | 1840.60021 | 509.758968 | 21.937611 | 0.000125 | 3.6905 |
[20]:
stats.plot()
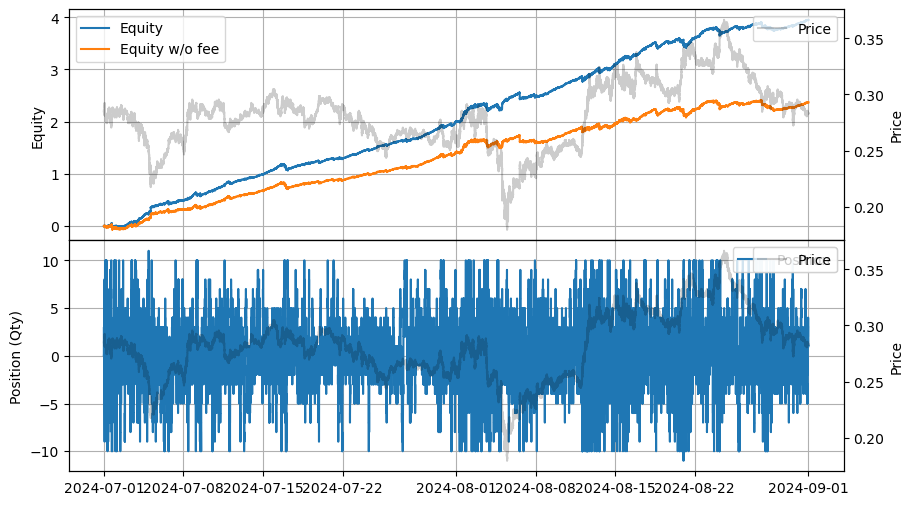
qty_thresholdを動的に制御し、スキュー値と統合するなど、より洗練されたアプローチを探ることもできます。たとえば、qty_threshold * (1 ± skew_val)のように、スキューが価格に適用されるのと同様に適用します。言い換えれば、前の例ではスプレッドが価格の観点で設定されていますが、キュー位置、注文の後ろのキュー、総キューなど、キューの観点でスプレッドを設定することができます。
さらに、固定間隔で反応するのではなく、各フィードの受信に応じて反応する方が効果的かもしれません。これにより、BBOの数量が急速に減少する場合に迅速に反応し、不利な選択を回避するのに役立ちます。このアプローチは、wait_next_feedメソッドを使用してテストできます。