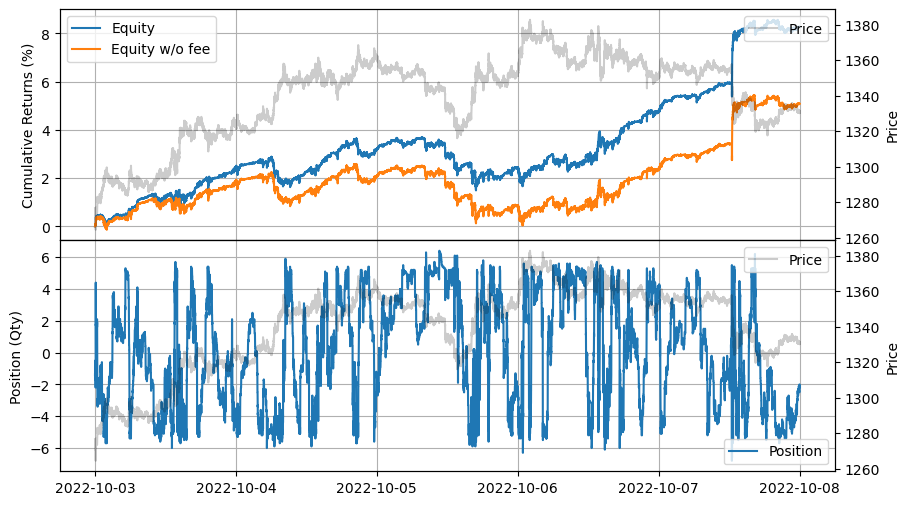
高頻度グリッドトレーディング
注: この例は教育目的のみであり、高頻度マーケットメイキングスキームの効果的な戦略を示しています。すべてのバックテストは、Binance Futuresで利用可能な最高のマーケットメイカーリベートである0.005%のリベートに基づいています。詳細については、Binance Upgrades USDⓢ-Margined Futures Liquidity Provider Program を参照してください。
単純な高頻度グリッドトレーディング
これは、ミッドプライスを中心にグリッド上に注文を投稿し続け、固定間隔と設定されたグリッド数を維持する高頻度バージョンのグリッドトレーディングです。
[1]:
import numpy as np
from numba import njit, uint64, float64
from numba.typed import Dict
from hftbacktest import BUY, SELL, GTX, LIMIT
@njit
def gridtrading(hbt, recorder):
asset_no = 0
tick_size = hbt.depth(asset_no).tick_size
grid_num = 20
max_position = 5
grid_interval = tick_size * 10
half_spread = tick_size * 20
# Running interval in nanoseconds.
while hbt.elapse(100_000_000) == 0:
# Clears cancelled, filled or expired orders.
hbt.clear_inactive_orders(asset_no)
depth = hbt.depth(asset_no)
position = hbt.position(asset_no)
orders = hbt.orders(asset_no)
best_bid = depth.best_bid
best_ask = depth.best_ask
mid_price = (best_bid + best_ask) / 2.0
order_qty = 0.1 # np.round(notional_order_qty / mid_price / hbt.depth(asset_no).lot_size) * hbt.depth(asset_no).lot_size
# Aligns the prices to the grid.
bid_price = np.floor((mid_price - half_spread) / grid_interval) * grid_interval
ask_price = np.ceil((mid_price + half_spread) / grid_interval) * grid_interval
#--------------------------------------------------------
# Updates quotes.
# Creates a new grid for buy orders.
new_bid_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position < max_position and np.isfinite(bid_price): # position * mid_price < max_notional_position
for i in range(grid_num):
bid_price_tick = round(bid_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_bid_orders[uint64(bid_price_tick)] = bid_price
bid_price -= grid_interval
# Creates a new grid for sell orders.
new_ask_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position > -max_position and np.isfinite(ask_price): # position * mid_price > -max_notional_position
for i in range(grid_num):
ask_price_tick = round(ask_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_ask_orders[uint64(ask_price_tick)] = ask_price
ask_price += grid_interval
order_values = orders.values();
while order_values.has_next():
order = order_values.get()
# Cancels if a working order is not in the new grid.
if order.cancellable:
if (
(order.side == BUY and order.order_id not in new_bid_orders)
or (order.side == SELL and order.order_id not in new_ask_orders)
):
hbt.cancel(asset_no, order.order_id, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_bid_orders.items():
# Posts a new buy order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_buy_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_ask_orders.items():
# Posts a new sell order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_sell_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
# Records the current state for stat calculation.
recorder.record(hbt)
return True
フィードデータファイルからフィードレイテンシを注文レイテンシとして使用する注文レイテンシを生成する方法については、Order Latency Data を参照してください。
[2]:
from hftbacktest import BacktestAsset, ROIVectorMarketDepthBacktest, Recorder
asset = (
BacktestAsset()
.data([
'data/ethusdt_20221003.npz',
'data/ethusdt_20221004.npz',
'data/ethusdt_20221005.npz',
'data/ethusdt_20221006.npz',
'data/ethusdt_20221007.npz'
])
.initial_snapshot('data/ethusdt_20221002_eod.npz')
.linear_asset(1.0)
.intp_order_latency([
'latency/feed_latency_20221003.npz',
'latency/feed_latency_20221004.npz',
'latency/feed_latency_20221005.npz',
'latency/feed_latency_20221006.npz',
'latency/feed_latency_20221007.npz'
])
.power_prob_queue_model(2.0)
.no_partial_fill_exchange()
.trading_value_fee_model(-0.00005, 0.0007)
.tick_size(0.01)
.lot_size(0.001)
.roi_lb(0.0)
.roi_ub(3000.0)
)
hbt = ROIVectorMarketDepthBacktest([asset])
recorder = Recorder(1, 5_000_000)
[3]:
%%time
gridtrading(hbt, recorder.recorder)
_ = hbt.close()
CPU times: user 6min 5s, sys: 9.08 s, total: 6min 15s
Wall time: 6min 16s
[4]:
from hftbacktest.stats import LinearAssetRecord
stats = LinearAssetRecord(recorder.get(0)).stats(book_size=10_000)
stats.summary()
[4]:
shape: (1, 11)
| start | end | SR | Sortino | Return | MaxDrawdown | DailyNumberOfTrades | DailyTurnover | ReturnOverMDD | ReturnOverTrade | MaxPositionValue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| datetime[μs] | datetime[μs] | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 |
| 2022-10-03 00:00:00 | 2022-10-07 23:59:50 | 18.265693 | 25.144025 | 0.082691 | 0.021906 | 9489.819672 | 127.266294 | 3.774836 | 0.00013 | 9140.288 |
[5]:
stats.plot()
スキューを伴う高頻度グリッドトレーディング
ポジションベースのスキューを組み込むことで、戦略のリスク調整後のリターンを向上させることができます。
[6]:
@njit
def gridtrading(hbt, recorder, skew):
asset_no = 0
tick_size = hbt.depth(asset_no).tick_size
grid_num = 20
max_position = 5
grid_interval = tick_size * 10
half_spread = tick_size * 20
# Running interval in nanoseconds.
while hbt.elapse(100_000_000) == 0:
# Clears cancelled, filled or expired orders.
hbt.clear_inactive_orders(asset_no)
depth = hbt.depth(asset_no)
position = hbt.position(asset_no)
orders = hbt.orders(asset_no)
best_bid = depth.best_bid
best_ask = depth.best_ask
mid_price = (best_bid + best_ask) / 2.0
order_qty = 0.1 # np.round(notional_order_qty / mid_price / hbt.depth(asset_no).lot_size) * hbt.depth(asset_no).lot_size
# The personalized price that considers skewing based on inventory risk is introduced,
# which is described in the well-known Stokov-Avalleneda market-making paper.
# https://math.nyu.edu/~avellane/HighFrequencyTrading.pdf
reservation_price = mid_price - skew * tick_size * position
# Since our price is skewed, it may cross the spread. To ensure market making and avoid crossing the spread,
# limit the price to the best bid and best ask.
bid_price = np.minimum(reservation_price - half_spread, best_bid)
ask_price = np.maximum(reservation_price + half_spread, best_ask)
# Aligns the prices to the grid.
bid_price = np.floor(bid_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
ask_price = np.ceil(ask_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
#--------------------------------------------------------
# Updates quotes.
# Creates a new grid for buy orders.
new_bid_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position < max_position and np.isfinite(bid_price): # position * mid_price < max_notional_position
for i in range(grid_num):
bid_price_tick = round(bid_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_bid_orders[uint64(bid_price_tick)] = bid_price
bid_price -= grid_interval
# Creates a new grid for sell orders.
new_ask_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position > -max_position and np.isfinite(ask_price): # position * mid_price > -max_notional_position
for i in range(grid_num):
ask_price_tick = round(ask_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_ask_orders[uint64(ask_price_tick)] = ask_price
ask_price += grid_interval
order_values = orders.values();
while order_values.has_next():
order = order_values.get()
# Cancels if a working order is not in the new grid.
if order.cancellable:
if (
(order.side == BUY and order.order_id not in new_bid_orders)
or (order.side == SELL and order.order_id not in new_ask_orders)
):
hbt.cancel(asset_no, order.order_id, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_bid_orders.items():
# Posts a new buy order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_buy_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_ask_orders.items():
# Posts a new sell order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_sell_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
# Records the current state for stat calculation.
recorder.record(hbt)
return True
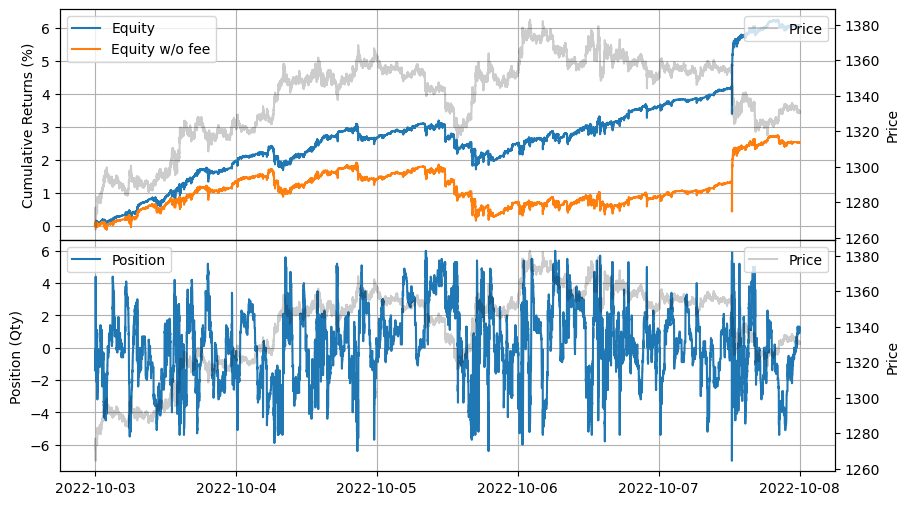
弱いスキュー
[7]:
hbt = ROIVectorMarketDepthBacktest([asset])
skew = 1
recorder = Recorder(1, 5_000_000)
gridtrading(hbt, recorder.recorder, skew)
hbt.close()
stats = LinearAssetRecord(recorder.get(0)).stats(book_size=10_000)
stats.summary()
[7]:
shape: (1, 11)
| start | end | SR | Sortino | Return | MaxDrawdown | DailyNumberOfTrades | DailyTurnover | ReturnOverMDD | ReturnOverTrade | MaxPositionValue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| datetime[μs] | datetime[μs] | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 |
| 2022-10-03 00:00:00 | 2022-10-07 23:59:50 | 18.363916 | 25.321583 | 0.060482 | 0.014831 | 10563.644529 | 141.707178 | 4.077966 | 0.000085 | 9409.12 |
[8]:
stats.plot()
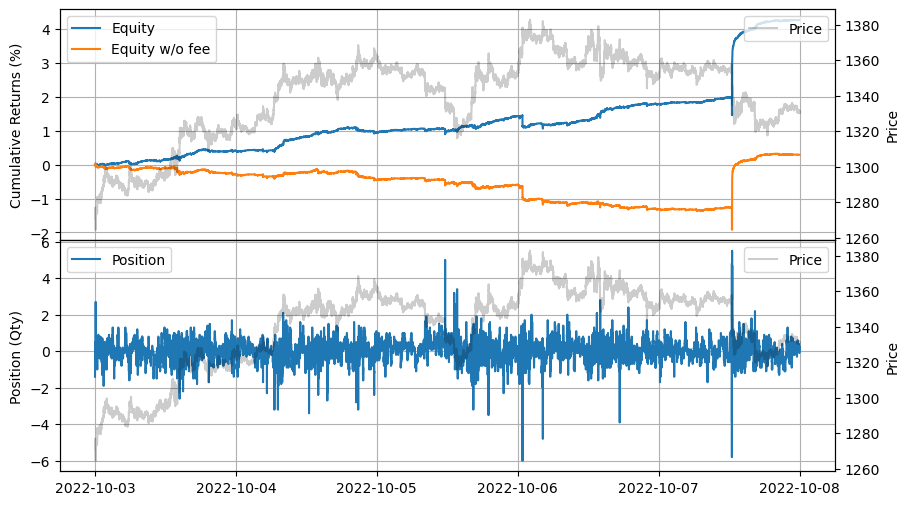
強いスキュー
強いスキューの下では、ポジションは弱いスキューの場合と比較してより制限されます。市場が急激に動くと、エクイティのスパイクが観察されることもあります。ただし、実際には注文レイテンシのためにこれが実現しない可能性があります。後で、注文レイテンシの影響を探り、実際の履歴注文レイテンシデータを使用する重要性を強調します。
[9]:
hbt = ROIVectorMarketDepthBacktest([asset])
skew = 10
recorder = Recorder(1, 5_000_000)
gridtrading(hbt, recorder.recorder, skew)
hbt.close()
stats = LinearAssetRecord(recorder.get(0)).stats(book_size=10_000)
stats.summary()
[9]:
shape: (1, 11)
| start | end | SR | Sortino | Return | MaxDrawdown | DailyNumberOfTrades | DailyTurnover | ReturnOverMDD | ReturnOverTrade | MaxPositionValue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| datetime[μs] | datetime[μs] | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 | f64 |
| 2022-10-03 00:00:00 | 2022-10-07 23:59:50 | 27.282302 | 47.25453 | 0.042574 | 0.005391 | 11838.874048 | 158.842253 | 7.897853 | 0.000054 | 8270.01 |
[10]:
stats.plot()
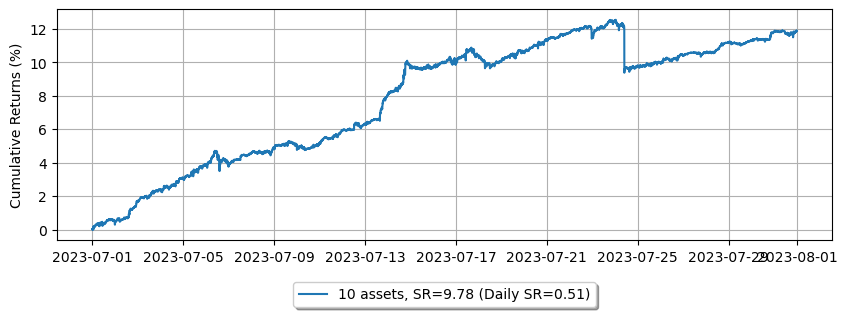
複数の資産
より良いパフォーマンスを達成するために、各資産に適したパラメータを見つける必要があるかもしれません。例として、ここでは単一のパラメータセットを使用して、複数の資産の組み合わせのパフォーマンスがどのようになるかを示します。
[11]:
@njit
def gridtrading(hbt, recorder, half_spread, grid_interval, skew, order_qty):
asset_no = 0
tick_size = hbt.depth(asset_no).tick_size
grid_num = 20
max_position = grid_num * order_qty
# Running interval in nanoseconds.
while hbt.elapse(100_000_000) == 0:
# Clears cancelled, filled or expired orders.
hbt.clear_inactive_orders(asset_no)
depth = hbt.depth(asset_no)
position = hbt.position(asset_no)
orders = hbt.orders(asset_no)
best_bid = depth.best_bid
best_ask = depth.best_ask
mid_price = (best_bid + best_ask) / 2.0
normalized_position = position / order_qty
# The personalized price that considers skewing based on inventory risk is introduced,
# which is described in the well-known Stokov-Avalleneda market-making paper.
# https://math.nyu.edu/~avellane/HighFrequencyTrading.pdf
reservation_price = mid_price - skew * normalized_position
# Since our price is skewed, it may cross the spread. To ensure market making and avoid crossing the spread,
# limit the price to the best bid and best ask.
bid_price = np.minimum(reservation_price - half_spread, best_bid)
ask_price = np.maximum(reservation_price + half_spread, best_ask)
# Ensures the grid interval aligns with the tick size, with the minimum set to the tick size.
grid_interval = max(np.round(grid_interval / tick_size) * tick_size, tick_size)
# Aligns the prices to the grid.
bid_price = np.floor(bid_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
ask_price = np.ceil(ask_price / grid_interval) * grid_interval
#--------------------------------------------------------
# Updates quotes.
# Creates a new grid for buy orders.
new_bid_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position < max_position and np.isfinite(bid_price): # position * mid_price < max_notional_position
for i in range(grid_num):
bid_price_tick = round(bid_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_bid_orders[uint64(bid_price_tick)] = bid_price
bid_price -= grid_interval
# Creates a new grid for sell orders.
new_ask_orders = Dict.empty(np.uint64, np.float64)
if position > -max_position and np.isfinite(ask_price): # position * mid_price > -max_notional_position
for i in range(grid_num):
ask_price_tick = round(ask_price / tick_size)
# order price in tick is used as order id.
new_ask_orders[uint64(ask_price_tick)] = ask_price
ask_price += grid_interval
order_values = orders.values();
while order_values.has_next():
order = order_values.get()
# Cancels if a working order is not in the new grid.
if order.cancellable:
if (
(order.side == BUY and order.order_id not in new_bid_orders)
or (order.side == SELL and order.order_id not in new_ask_orders)
):
hbt.cancel(asset_no, order.order_id, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_bid_orders.items():
# Posts a new buy order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_buy_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
for order_id, order_price in new_ask_orders.items():
# Posts a new sell order if there is no working order at the price on the new grid.
if order_id not in orders:
hbt.submit_sell_order(asset_no, order_id, order_price, order_qty, GTX, LIMIT, False)
# Records the current state for stat calculation.
recorder.record(hbt)
return True
[12]:
from hftbacktest import BUY_EVENT, SELL_EVENT
latency_data = np.concatenate(
[np.load('latency/live_latency_{}.npz'.format(date))['data'] for date in range(20230701, 20230732)]
)
def backtest(args):
asset_name, asset_info = args
# Obtains the mid-price of the assset to determine the order quantity.
snapshot = np.load('data/{}_20230630_eod.npz'.format(asset_name))['data']
best_bid = max(snapshot[snapshot['ev'] & BUY_EVENT == BUY_EVENT]['px'])
best_ask = min(snapshot[snapshot['ev'] & SELL_EVENT == SELL_EVENT]['px'])
mid_price = (best_bid + best_ask) / 2.0
asset = (
BacktestAsset()
.data(['data/{}_{}.npz'.format(asset_name, date) for date in range(20230701, 20230732)])
.initial_snapshot('data/{}_20230630_eod.npz'.format(asset_name))
.linear_asset(1.0)
.intp_order_latency(latency_data)
.log_prob_queue_model2()
.no_partial_fill_exchange()
.trading_value_fee_model(-0.00005, 0.0007)
.tick_size(asset_info['tick_size'])
.lot_size(asset_info['lot_size'])
.roi_lb(0)
.roi_ub(mid_price * 5)
)
hbt = ROIVectorMarketDepthBacktest([asset])
# Sets the order quantity to be equivalent to a notional value of $100.
order_qty = max(round((100 / mid_price) / asset_info['lot_size']), 1) * asset_info['lot_size']
half_spread = mid_price * 0.0008
grid_interval = mid_price * 0.0008
skew = mid_price * 0.000025
recorder = Recorder(1, 50_000_000)
gridtrading(hbt, recorder.recorder, half_spread, grid_interval, skew, order_qty)
hbt.close()
recorder.to_npz('stats/gridtrading_{}.npz'.format(asset_name))
[13]:
%%capture
import json
from multiprocessing import Pool
with open('assets.json', 'r') as f:
assets = json.load(f)
with Pool(16) as p:
print(p.map(backtest, list(assets.items())))
[14]:
import polars as pl
from hftbacktest.stats import LinearAssetRecord
equity_values = {}
for asset_name in assets.keys():
data = np.load('stats/gridtrading_{}.npz'.format(asset_name))['0']
stats = (
LinearAssetRecord(data)
.resample('5m')
.stats()
)
equity = stats.entire.with_columns(
(pl.col('equity_wo_fee') - pl.col('fee')).alias('equity')
).select(['timestamp', 'equity'])
equity_values[asset_name] = equity
[15]:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
fig.set_size_inches(10, 3)
legend = []
net_equity = None
for i, equity in enumerate(list(equity_values.values())):
asset_number = i + 1
if net_equity is None:
net_equity = equity['equity'].clone()
else:
net_equity += equity['equity'].clone()
if asset_number % 10 == 0:
# 2_000 is capital for each trading asset.
net_equity_df = pl.DataFrame({
'cum_ret': (net_equity / asset_number) / 2_000 * 100,
'timestamp': equity['timestamp']
})
net_equity_rs_df = net_equity_df.group_by_dynamic(
index_column='timestamp',
every='1d'
).agg([
pl.col('cum_ret').last()
])
pnl = net_equity_rs_df['cum_ret'].diff()
sr = pnl.mean() / pnl.std()
ann_sr = sr * np.sqrt(365)
plt.plot(net_equity_df['timestamp'], net_equity_df['cum_ret'])
legend.append('{} assets, SR={:.2f} (Daily SR={:.2f})'.format(asset_number, ann_sr, sr))
plt.legend(
legend,
loc='upper center', bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, -0.15),
fancybox=True, shadow=True, ncol=3
)
plt.grid()
plt.ylabel('Cumulative Returns (%)')
[15]:
Text(0, 0.5, 'Cumulative Returns (%)')